4.1 조건문 형식
* Conditional Statement : 조건문
- 어떤 경우에는 1만 실행, 어떤 경우에는 a나 b만 실행되도록, (* if 안의 값은 booelan(true/false)만 올 수 있다.)
> if(true)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
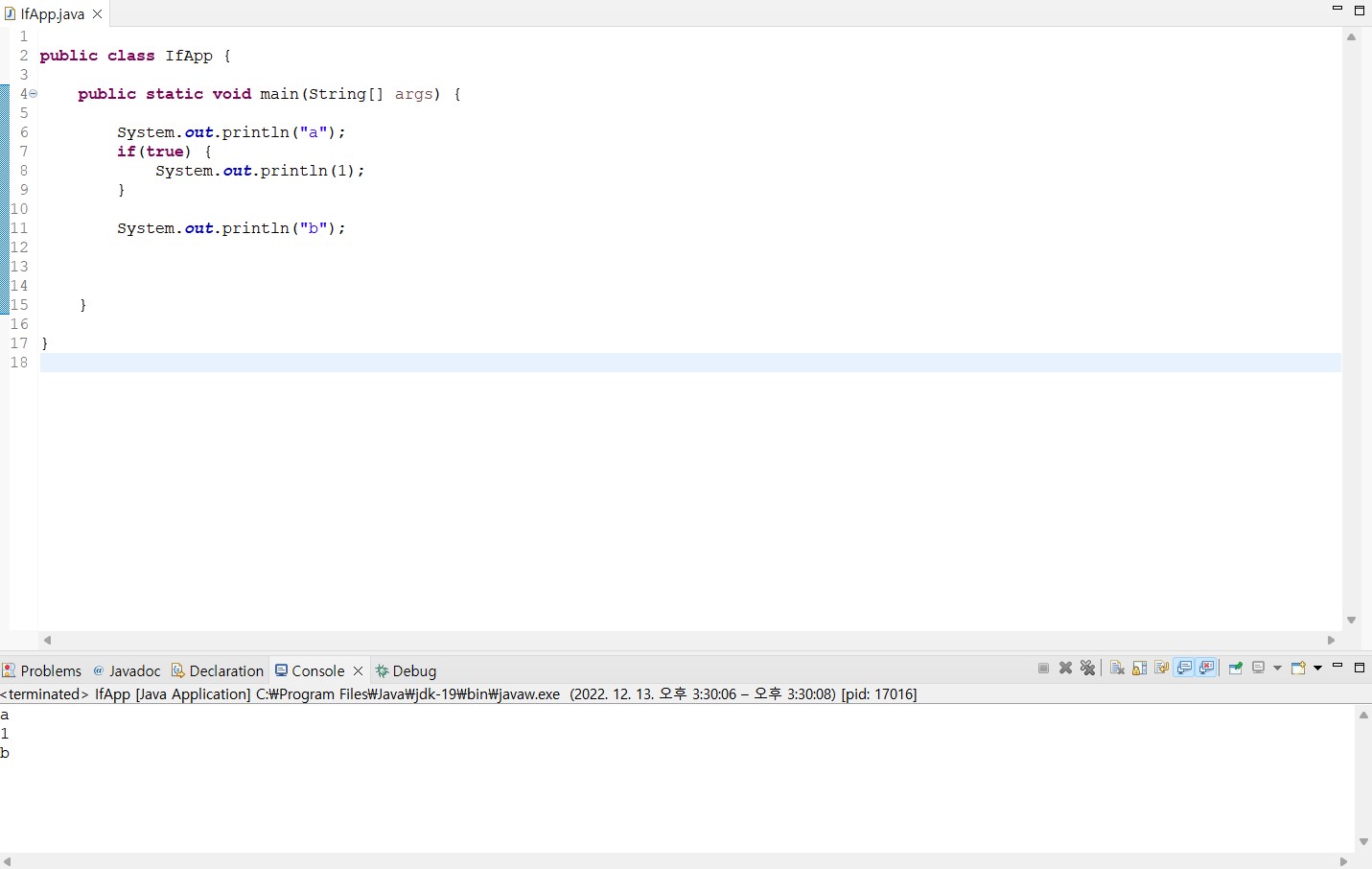
public class IfApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("a");
if(true) {
System.out.println(1);
}
System.out.println("b");
}
}
|
cs |
> 괄호 안의 값이 true라면, 중괄호 안의 값이 실행이 된다.
> if(false)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
public class IfApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("a");
if(false) {
System.out.println(1);
}
System.out.println("b");
}
}
|
cs |
> 괄호 안의 값이 false라면, 중괄호 안의 값이 실행이 되지 않음

>> 여기서 밑줄은 데드코드 : 영원히 실행될 수 없는 코드!
- 조건문의 가장 기본 형식
> if(boolean) : boolean이 true냐 false냐에 따라 중괄호의 값이 실행이 될 수도, 안될수도
- true일 때는 1이, false일 때는 2가 실행되게 코드를 짤 수도 있음
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
public class IfApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("a");
if(true) {
System.out.println(1);
}else {
System.out.println(2);
}
System.out.println("b");
}
}
|
cs |

- 계속 else, else로 표시할 수도 있지만 더 간단하게 정리해서 표현하면,
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
public class IfApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("a");
if(false) {
System.out.println(1);
} else if(true) {
System.out.println(2);
} else {
System.out.println(3);
}
System.out.println("b");
}
}
|
cs |
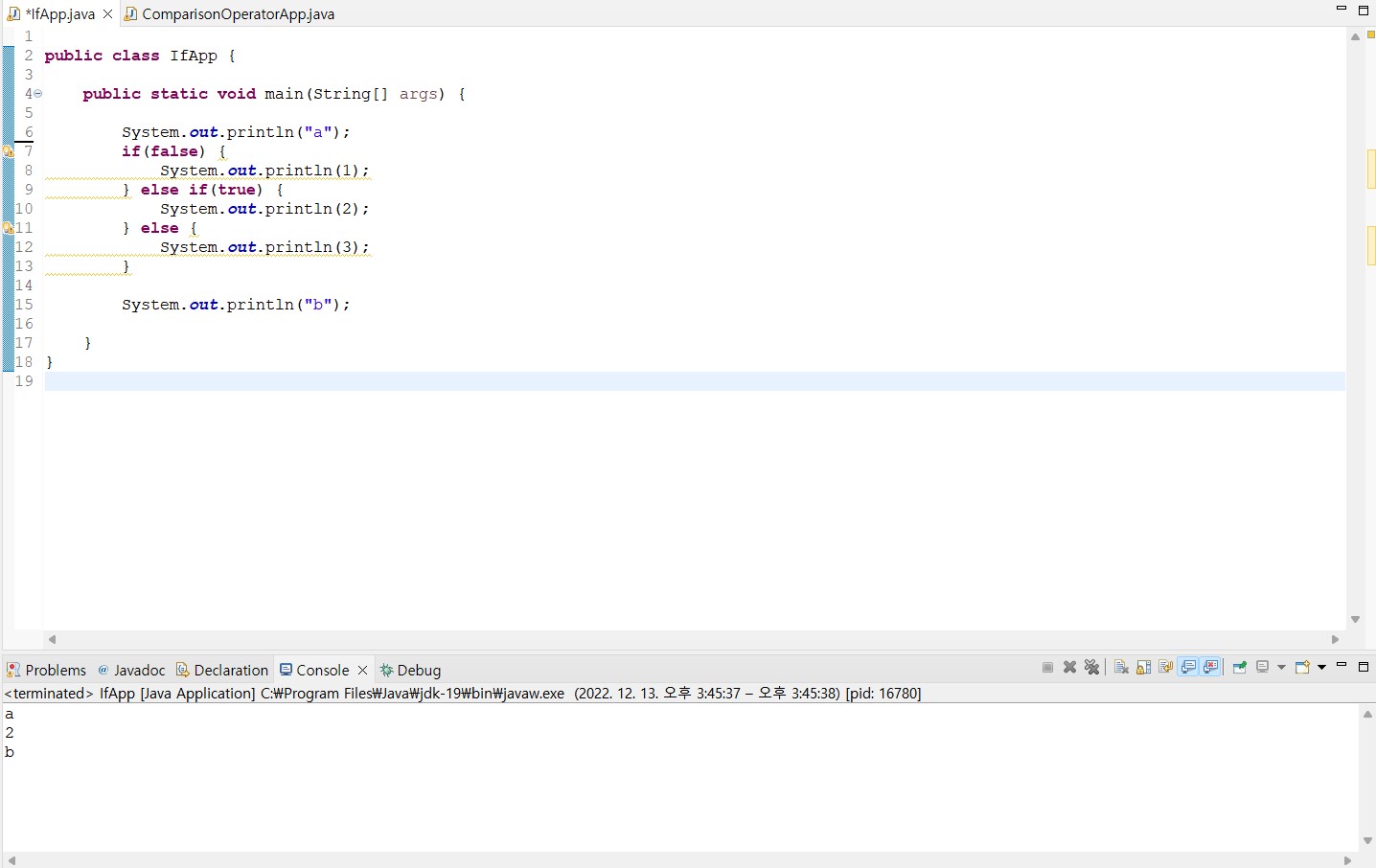
> if(false) : 의 값은 false이기 때문에 절대 실행되지 않음
> else 값도 else if(true)이기 때문에, 절대 실행되지 않음
>> 위의 장황하게 작성된 코드는 결국, 아래와 똑같음(의미가 없음)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
public class IfApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("a");
if(false) {
System.out.println(1);
System.out.println(2);
} else {
System.out.println(3);
}
System.out.println("b");
}
}
|
cs |
4.2 조건문 응용
> 위의 장황한 코드가 의미가 있기 위해서는 if(false)> 의 boolean의 위치가 true일 때도, false일 때도 있어야 함
- 로그인 어플리케이션 만들기 \
> 프로그램을 실행할 때 egoing이라는 텍스트를 주면 hi master라고 뜨고,
egoing이 아닌 다른 값을 주면 who are you라는 텍스트가 뜨도록.
- 먼저, AuthApp이라는 파일의 실행 방식을 바꿔줌
> 한 번은 실행을 시킴 > 재생 메뉴의 Run Configurations > Arguments의 Program arguments에 egoing 입력
- 디버깅으로 확인할 때, 바로 Who are you? 로 들어가는 문제를 해결하려면..
if(inputId == id) { 가 아닌, if(inputId.equals(id)) { 가 되어야 함
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
public class AuthApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String id = "egoing";
String inputId = args[0];
System.out.println("Hi.");
// if(inputId == id) {
if(inputId.equals(id)) {
System.out.println("Master!");
} else {
System.out.println("Who are you?");
}
}
}
|
cs |

>> if이 반환하는 값은 boolean이고, 그 boolean이 무엇이냐에 따라 다른 값이 나오게 된다.
4.3 조건문 응용
- 이번에는 id값에 이어서 비밀번호를 체크할 수 있도록
> id가 egoing이고 비밀번호가 1111일 때, master가 뜨도록!

|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
public class AuthApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String id = "egoing";
String inputId = args[0];
String pass = "1111";
String inputPass = args[1];
System.out.println("Hi.");
// // if(inputId == id) {
// if(inputId.equals(id)) {
// if(inputpass.equals(pass)) {
// System.out.println("Master!");
// } else {
// System.out.println("Wrong password!");
// }
// } else {
// System.out.println("Who are you?");
// }
if(inputId.equals(id) && inputPass.equals(pass)) {
System.out.println("Master!");
} else {
System.out.println("Who are you?");
}
}
}
|
cs |

* 프로그래밍이란 프로그램이 input에 반응해서 output을 만들어내는 것
> input으로는 argument, file, network, audio, program 등
> 프로그램이 순차적으로 실행해서 output을 내는 것인데,
이때 조건문을 쓰게 되면
input이 무엇이냐에 따라 프로그램을 다르게 동작하게 만들어서 그에 따른 output을 만들 수 있음
'Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 생활코딩 JAVA 제어문 - 반복문과 배열 (0) | 2022.12.15 |
|---|---|
| 생활코딩 JAVA 제어문 - 비교연산자(== vs equals) (0) | 2022.12.13 |
| 생활코딩 JAVA 제어문 - 비교연산자 (0) | 2022.12.13 |
| 생활코딩 JAVA 제어문 - Boolean data type (0) | 2022.12.13 |
| 생활코딩 java 입문편 - 8일차 (0) | 2022.12.07 |